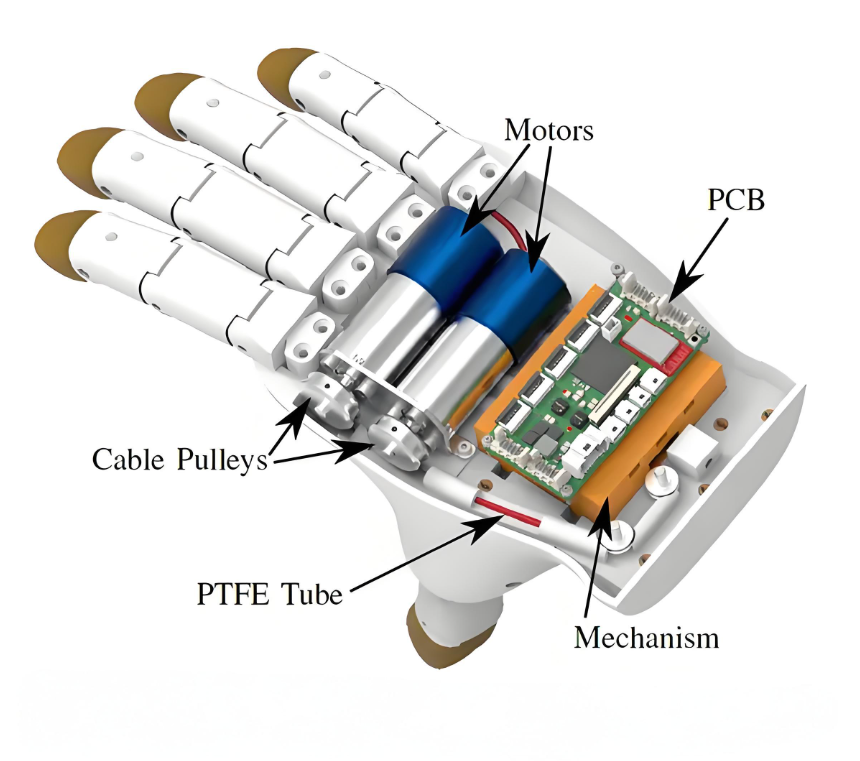
In medical rehabilitation equipment, PCB has an important application, mainly reflected in the following aspects:
Precise control systems
Medical rehabilitation equipment requires precise control, and PCB carries electronic components to realize this function. For example, in rehabilitation robots, PCBs control the trajectory, force, and speed to ensure that the rehabilitation training is carried out according to the preset program.
In medical monitoring equipment, PCB realizes real-time monitoring of patient’s vital signs and data processing, providing doctors with accurate diagnosis basis.
High-performance microprocessors, sensors, and controllers, as well as high-precision analog and digital circuit design, achieve precise control.
Biocompatibility
Medical rehabilitation equipment in direct contact with the human body, PCB materials need to have good biocompatibility, and can not have adverse effects on the human body, such as allergies, toxicity, and so on.
Usually used in line with biomedical standards of materials, such as polyimide, ceramics, etc., with good insulation properties, mechanical strength, and heat resistance, while good biocompatibility.
Strict control of process parameters during the manufacturing process to avoid the introduction of substances that adversely affect the human body.
Efficient Data Processing
Medical rehabilitation equipment needs to deal with a large amount of medical data, such as patient physiological signals, and rehabilitation training data, PCB must have efficient data processing capabilities.
The use of high-performance microprocessors, digital signal processors, and memory, as well as a high-speed data transmission interface.
Parallel processing, distributed computing, and other technologies can be used to improve data processing efficiency and speed.
Accurate control systems, biocompatibility, and efficient data processing are the key requirements for PCB application in medical rehabilitation equipment, and PCB technology will play a greater role in the field of medical rehabilitation in the future.